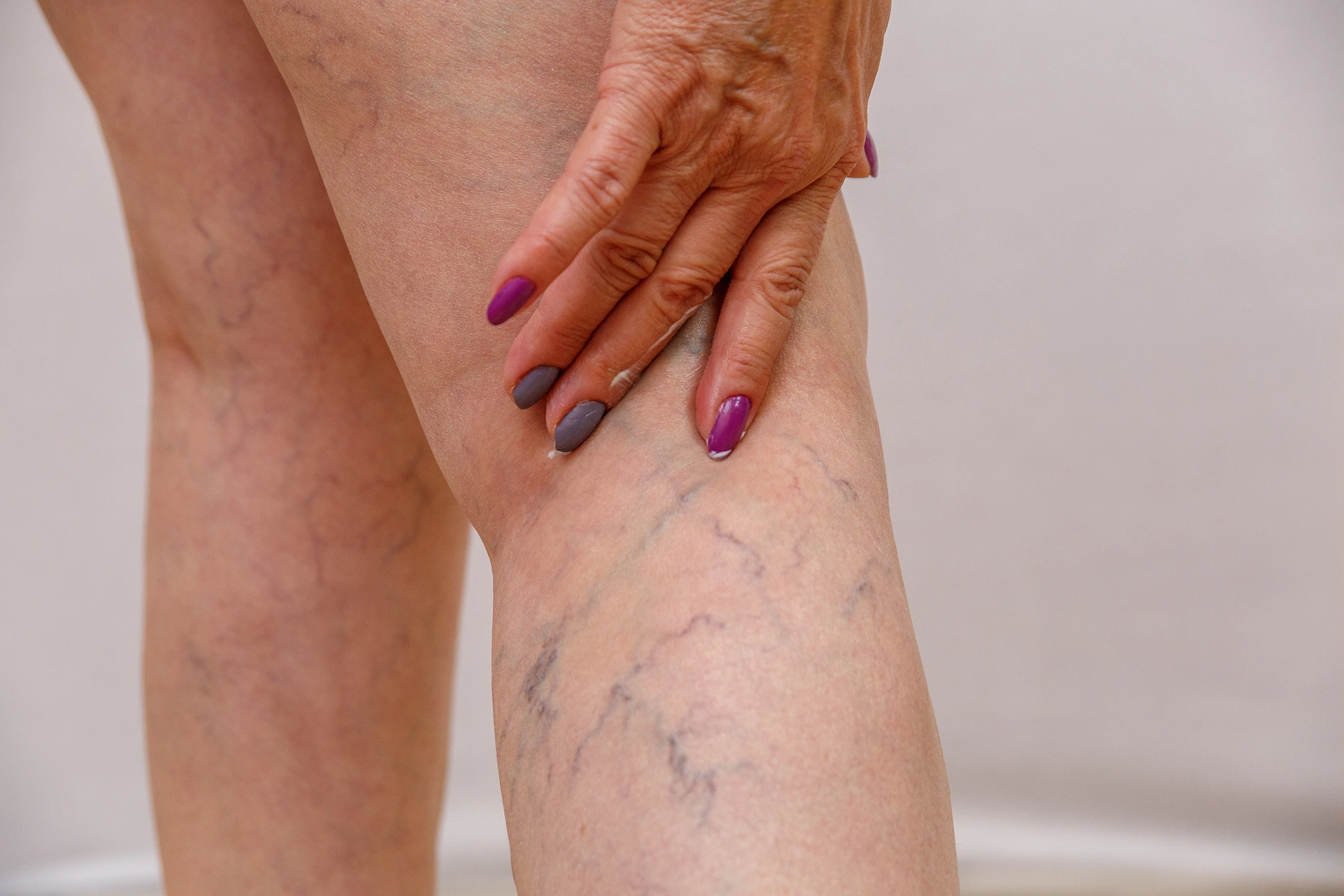
Varicose veins are easily distinguishable by their bulging and twisted appearance with a blue or dark purple color. They also commonly appear protruding and often feel soft or tender when touched on the skin’s surface. But in some cases, an enlarged vein can also feel hard or lumpy which could potentially point to a varicose veins complication.
So what does it mean when you have hard varicose veins? It could indicate the presence of a blood clot in the superficial vein or deep vein in the lower leg. The hardness of the veins may also be accompanied by other uncomfortable symptoms such as warmth and tenderness in the affected area, swelling, pain, and redness of the surrounding skin. If left untreated, it could lead to disabling conditions like superficial thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis.
What Do Hard Varicose Veins Mean?
Varicose veins and spider veins are common vascular disorders that can affect almost all individuals at some point in their lives. They’re primarily caused by chronic venous insufficiency which is a medical condition where the valves in your leg vein aren’t allowing blood to flow properly back to the heart. Other risk factors that can lead to this venous disease are old age, genetics, hormones, obesity, and prolonged hours of sitting or standing.
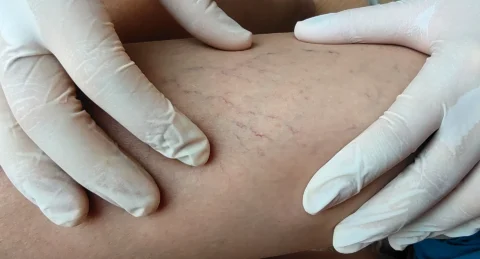
This vein disease usually forms just beneath the skin and you can easily palpate them to examine its shape, texture, and firmness. Normally, varicose veins can feel soft or tender to the touch but having enlarged veins can be associated with a distinct hardened or lumpy sensation.
The formation of a blood clot in the veins is one of the main reasons why varicose veins can feel hard. In fact, having varicose veins is a risk factor for developing clots because the blood vessels are in a damaged or weakened state. This results in the pooling of blood within the veins which increases the likelihood of the vein wall breaking open and causing blood clots.
Some people with varicose veins are also at a higher risk for a venous leg ulcer. This condition occurs from poor blood circulation in your leg veins and can lead to clotting problems. According to studies, leg sores are a potential long-term risk of venous diseases and can make your leg feel swollen and hard.
What Happens When A Varicose Veins Harden?
A blood clot isn’t an uncommon phenomenon with varicose veins, but it may result in serious complications if not treated promptly. Depending on their location, there are different kinds of blood clot disorders that can occur from untreated varicose veins. Here’s an overview of the differences between the common types of blood clots in the leg vein:
| Superficial thrombophlebitis | Deep vein thrombosis | |
| Description | Also known as phlebitis, it refers to vein inflammation below the skin surface that occurs from the formation of a blood clot. | This describes the presence of a blood clot in the deep vein or enlarged vein in the legs. |
| Location | Blood clot forms in the superficial veins and usually affects a small area of the leg. | It commonly affects the lower legs but can also occur in the deep veins in the thigh, pelvis, and arms |
| Accompanying signs and symptoms | Skin redness, warmth, tenderness, lower leg pain, and hardening of the varicose vein. | Leg throbbing, muscle cramps, pain, swelling, tenderness, and skin discoloration. |
| Overview of risk | According to studies, superficial thrombophlebitis can occur in about 75% to 88% of cases of varicose veins. | Compared to phlebitis, DVT is a more serious complication but it rarely occurs with small varicose veins. The risk may be higher in people with severe varicose veins. |
| Outlook | It’s usually a short-lived condition with symptoms that can last for 1 to 2 weeks. However, the hardening of the varicose vein can remain longer and require proper treatment. | Its symptoms can go away on their own but there’s a chance of recurrence if the venous disease isn’t addressed or managed properly. |
Are Hard Varicose Veins Dangerous?

Varicose veins aren’t specifically life-threatening but their symptoms can progress and affect your quality of life. In terms of blood clot disorders, DVT and phlebitis are considered thrombus which is a clot that remains stationary in the affected vein. They block the normal blood flow which results in the visible swelling and hardening of the varicose veins.
There are rare cases when clots from DVT and superficial thrombophlebitis break loose and move to other parts of the body. This can lead to more serious events such as pulmonary embolism and peripheral venous disease.
- Pulmonary embolism from DVT and varicose veins – Blood clots found in the deep leg veins move through the bloodstream and reach the lungs, potentially blocking proper blood circulation in the heart and other organs. This could cause symptoms like excessive sweating, dizziness, lightheadedness, and leg swelling.
- Peripheral venous disease and varicose veins – PVD is a circulatory disorder that can occur when the blood vessels are blocked by a clot and fail to transport oxygen-rich blood to the heart. It can occur in the arms and legs and can be found in people with varicose veins. Its symptoms can include numbness, muscle heaviness, discoloration of the lower extremities, limited mobility, and severe pain.
What to Do About Hard Varicose Veins: Possible Treatment Options
The good thing about varicose veins and blood clots is that they can be easily treated provided that they’re immediately diagnosed by a healthcare provider or vein doctor. Here are some of the possible treatments for hard varicose veins:
- Medications: If your doctor finds a blood clot in your superficial or deep veins, they may prescribe blood-thinning or clot-dissolving medications to help break up the clots in the blood vessel. They may also prevent the existing clots from growing further and improve the flow of blood through your veins.
- Compression Stockings: Doctors can also recommend wearing graduated compression stockings to manage leg swelling and pain from large varicose veins. Wearing them regularly may help the symptoms of superficial thrombophlebitis and lower the risk for DVT.
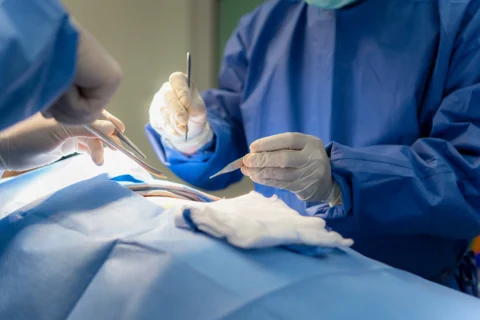
- Endovenous Ablation: Superficial and large varicose veins can also respond well to endovenous ablation procedures. This vein treatment option uses either laser or radiofrequency energy to heat the walls of the damaged vein which can seal it off and block the passage of blood, redirecting the circulation to a nearby healthy vein.
Experience Safe Varicose Vein Treatments at The Vein Center Doctor

Varicose veins aren’t always a cause for serious concern. But when you begin noticing swelling, warmth, and hardness in the affected area, it could be a sign of a blood clot that you need to immediately address. You can prevent blood clots and improve varicose vein symptoms with minimally invasive remedies such as endovenous ablation, compression therapy, and medications.
At Vein Center Doctor, we offer specialized treatments for varicose and spider vein removal and management of other venous diseases. We have a team of highly trained providers who can perform safe vein ablation, sclerotherapy, and VenaSeal procedures to provide lasting relief from your varicose vein condition. Book a consultation with us or learn more about our other services by contacting us today.