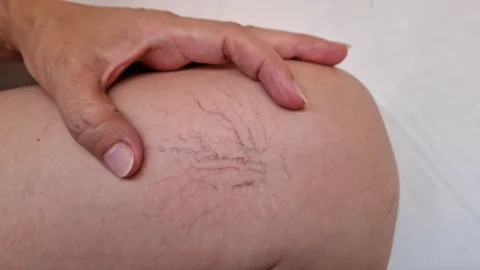
Spider veins on only one leg often stem from underlying issues like DVT, venous insufficiency, or injury, but treatable options exist to manage their appearance and prevent progression.
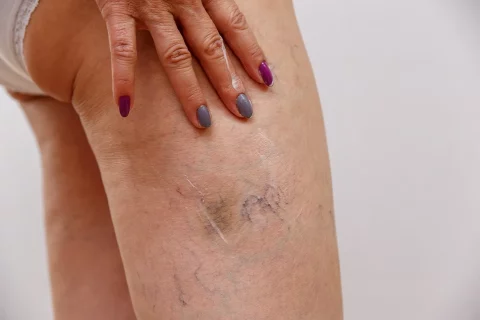
If you’ve noticed a web-like pattern of reddish veins on just one of your legs, you may be wondering what’s causing this asymmetric appearance. Spider veins, also called telangiectasias, are small dilated blood vessels that can develop close to the surface of the skin. While spider veins can occur on both legs, it’s not uncommon for them to appear on just one leg.
What Underlying Medical Conditions Can Cause Spider Veins on One Leg?
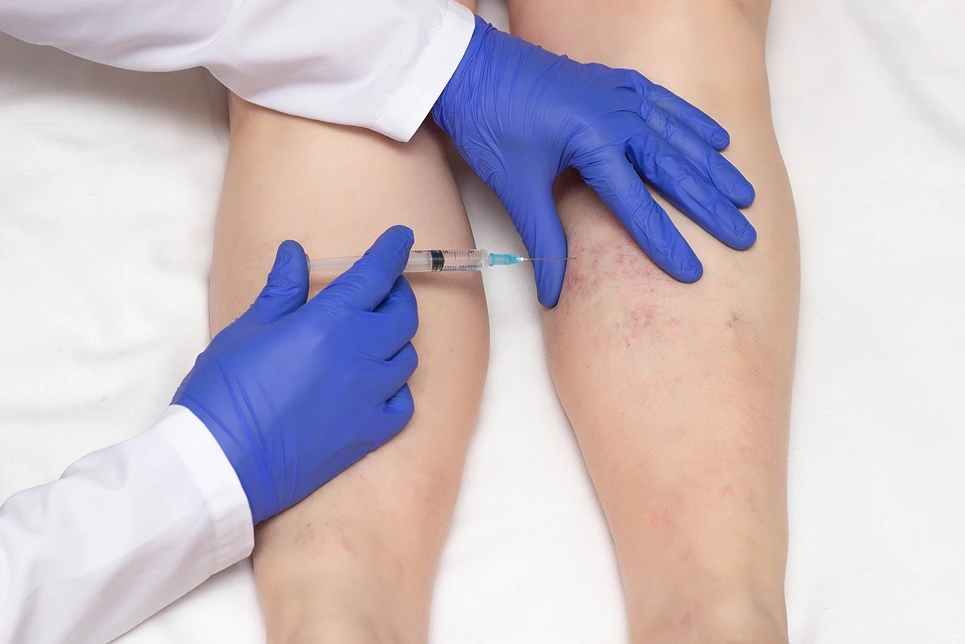
There are a few potential medical explanations for why spider veins may selectively affect one leg:
Prior Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A DVT that occurred in one leg can sometimes lead to damage of the valves inside the deeper veins. Faulty valves allow blood to pool and build excessive pressure in the superficial veins, causing them to dilate and take on the characteristic spider vein appearance. If you have a history of DVT, this is likely the reason for unilateral spider veins.
Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency refers to improperly functioning veins that have trouble carrying blood from the legs back to the heart. This condition often arises from a combination of damaged valves and weakened vein walls. The increased pressure in the veins of the affected leg forces fluid and blood to seep into the surrounding tissue. Spider veins can develop as a result of the unrelieved pressure.
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome
This condition causes varicose veins to form around the ovaries or prostate in women and men, respectively. The excess pressure in the pelvic veins can back up into the leg on the same side of the body, producing unilateral spider veins. Pain, discomfort, and heavy feelings in the pelvis are symptoms of pelvic congestion syndrome.
Previous Leg Injury or Trauma
An injury that causes blood vessels in one leg to rupture and dilate or leads to localized inflammation around the veins can ultimately lay the groundwork for spider veins. The resulting damage to the blood vessels can cause them to improperly widen over time.
What are the Specific Risk Factors for Spider Veins on One Leg?
Some contributing factors seem to raise the risk of spider veins occurring on just one leg rather than in a bilateral distribution:
- Having a history of blood clots, especially a DVT in one leg
- Jobs or activities requiring long periods of standing on just one leg
- Trauma from surgery or injury that damaged veins in one leg
- Obesity, which can increase pressure on the veins unilaterally if weight distribution is uneven
- High estrogen levels, such as during pregnancy, that amplified varicose veins in one leg
The underlying causes may also predispose certain individuals to unilateral spider veins. For example, a circulation issue like venous insufficiency or a pelvic tumor mainly impacting drainage on one side of the body.
How Can I Tell if Spider Veins are a Sign of Something More Serious?

Spider veins on their own are typically not a major health concern. But in some cases, they may indicate an underlying medical issue that requires further evaluation:
Pay attention to other symptoms occurring with the spider veins:
- Swelling, pain, cramping, or heaviness in the affected leg
- Visible varicose veins accompanying the spider veins
- Discoloration or ulcers on the skin around the spider veins
- Sudden onset of numerous spider veins rather than a gradual appearance
Consider your personal and family medical history:
- Previous DVT or pelvic congestion syndrome
- Family history of vein disease or circulation disorders
- Current pregnancy or recent childbirth
- Chronic conditions like obesity, hypertension, or diabetes
Seek medical advice if spider veins:
- Appear alongside other venous symptoms
- Seem to have arisen for no reason
- Develop rapidly or multiply quickly
- Only affect one leg
Getting a professional opinion can identify any underlying condition and determine appropriate treatment.
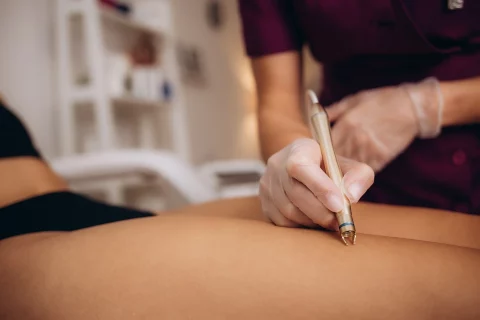
What Are the Best Treatment Options for Spider Veins on One Leg?
Treating spider veins on a single leg gives physicians the chance to develop a tailored treatment plan. Here are some of the top treatment choices:
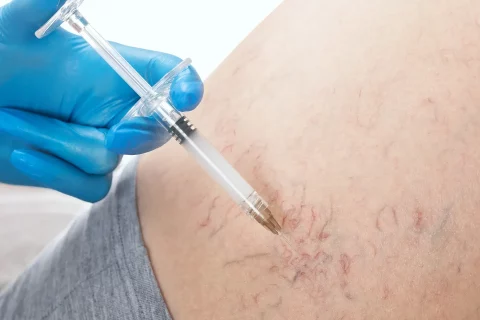
Sclerotherapy
This is the gold standard approach for eliminating spider veins. It involves injecting a liquid chemical into the veins, causing them to scar and eventually fade. When treating just one leg, the doctor can precisely target each vein.
Laser Therapy
A strong beam of light is used to destroy spider veins. Laser energy can be focused on the affected leg without needing to treat the other leg unnecessarily.
Ambulatory Phlebectomy
Tiny incisions allow the surgeon to remove spider veins through hook-like instruments on just the involved leg. This minimally invasive technique is done under local anesthesia.
Compression Stockings
Wearing medical-grade compression stockings daily applies helpful pressure to improve circulation in the leg with spider veins. This can help minimize swelling and discomfort.
Lifestyle Changes
Diet, exercise, and elevating the affected leg can all help reduce pressure on the veins to prevent spider veins from worsening.
These treatments offer precise, effective ways to eliminate spider veins on one leg without impacting the other leg. Your doctor will advise the best approach based on your specific case.
Can I Prevent Spider Veins From Spreading or Getting Worse?
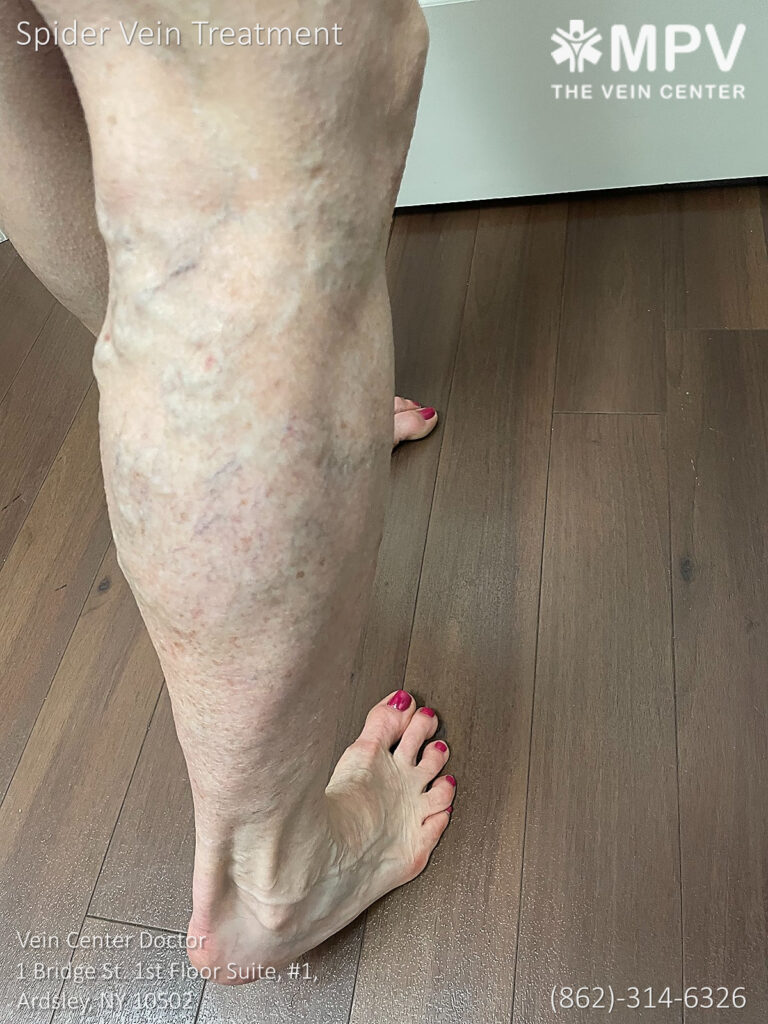
Taking proactive measures may stop spider veins on one leg from proliferating or appearing on the other leg:
- Wear compression stockings regularly to improve circulation
- Exercise consistently to strengthen leg muscles and venous return
- Lose excess weight to avoid added pressure on the veins
- Limit prolonged standing or sitting without breaks
- Elevate your legs when possible to let gravity drain the veins
- Avoid constrictive clothing around the legs and waist
- Consider vein-toning supplements like vitamin C, rutin, or butcher’s broom
Making lifestyle changes to ease the burden on your veins can help contain spider veins or varicose veins to just one leg. But new spider veins can occasionally emerge due to age, hormones, and genetics. Seeking treatment right away offers the best chance of stopping their spread.
Conclusion
Spider veins isolated to just one leg are often attributable to an underlying condition putting excess strain on the veins. DVT, venous insufficiency, pelvic congestion syndrome, or previous injury can all cause asymmetrical spider veins in the legs.
While not usually dangerous on their own, spider veins may sometimes indicate advanced vein disease. Treatments like sclerotherapy injections effectively target spider veins on a single leg.
Lifestyle measures and compression stockings can help prevent the spread of spider veins and improve comfort in the affected leg. Consulting a vein specialist allows for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan for addressing spider veins appearing unilaterally on just one leg.