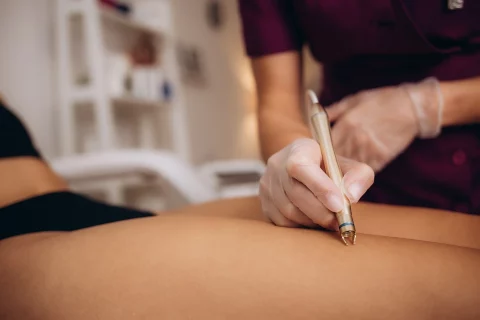
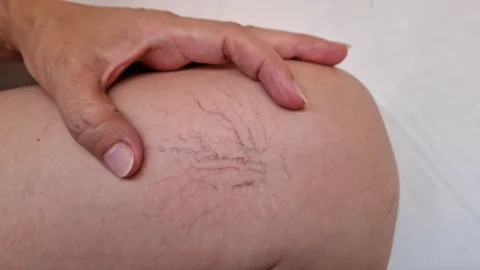
Understand the common and rare side effects of spider vein injections to ensure a smooth and safe recovery process.

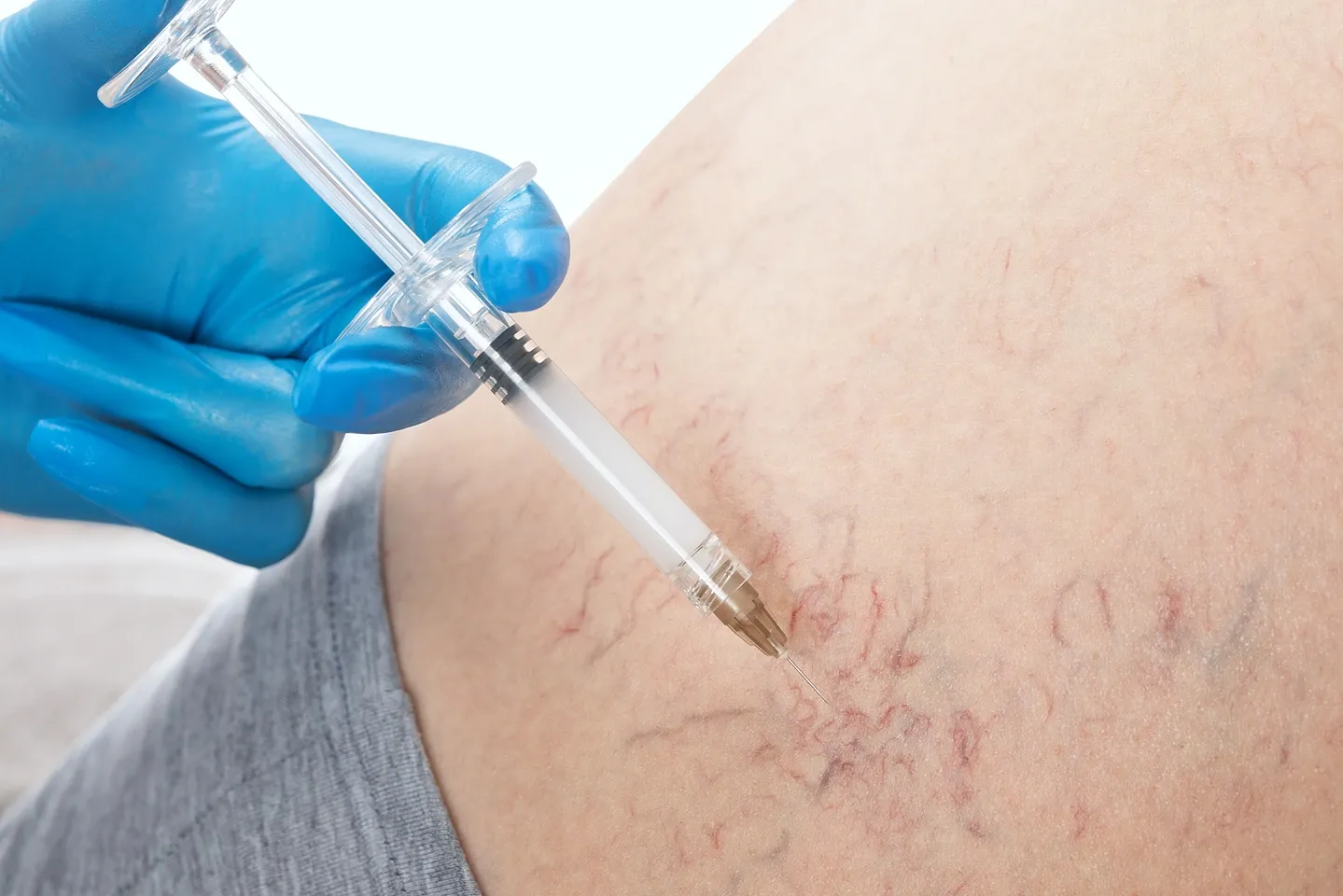
Common side effects of spider veins injections include bruising, swelling, and inflammation at the injection site, which usually resolve within a few days to a week. You might also experience temporary skin reactions like redness, mild itching, and the development of new tiny blood vessels known as “matting.”
While rare, serious complications such as allergic reactions, blood clots, and phlebitis can occur. To minimize risks, wearing compression stockings and following your doctor’s advice is crucial.
Living with unwanted veins is a thing of the past, when you can simply schedule a free consultation with Vein Center Doctor and find your ideal solution today.
Common Side Effects of Spider Vein Injections
You may also experience stinging or a burning sensation at the injection site, as well as some swelling and discoloration.
These symptoms are usually short-lived and resolve on their own. Inflammation is another common side effect, characterized by raised, reddish spots that resemble bug bites or small sores, which generally fade within 24 hours.
To minimize these side effects, wearing compression stockings immediately after the procedure can be helpful.
Following your doctor’s post-procedure instructions carefully can also reduce the risk of these common side effects.
If you experience any persistent or severe symptoms, it’s important to discuss them with your doctor to determine if further treatment or alternative strategies are necessary.
Temporary Skin Reactions
Temporary skin reactions are a common occurrence. One of the most frequent temporary skin reactions is temporary redness or discoloration at the injection site. This redness is usually a result of the skin’s reaction to the sclerosing solution and typically resolves on its own within a few days.
You may also experience itching at the injection site, which can be mild and temporary. This itching is a response to the irritation caused by the sclerosing agent and usually subsides without further treatment.
Swelling of the legs or ankles can occur temporarily, and some patients might notice the development of new, tiny blood vessels near the treated area, a condition known as “matting.” These new blood vessels often resolve over time but may require additional treatments in some cases].
You might also notice stinging or pain at the injection sites, and some people may develop raised red areas similar to hives, although these usually disappear within a day or so.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions to minimize these temporary reactions and ensure the best possible outcome from the treatment.
Allergic Reactions
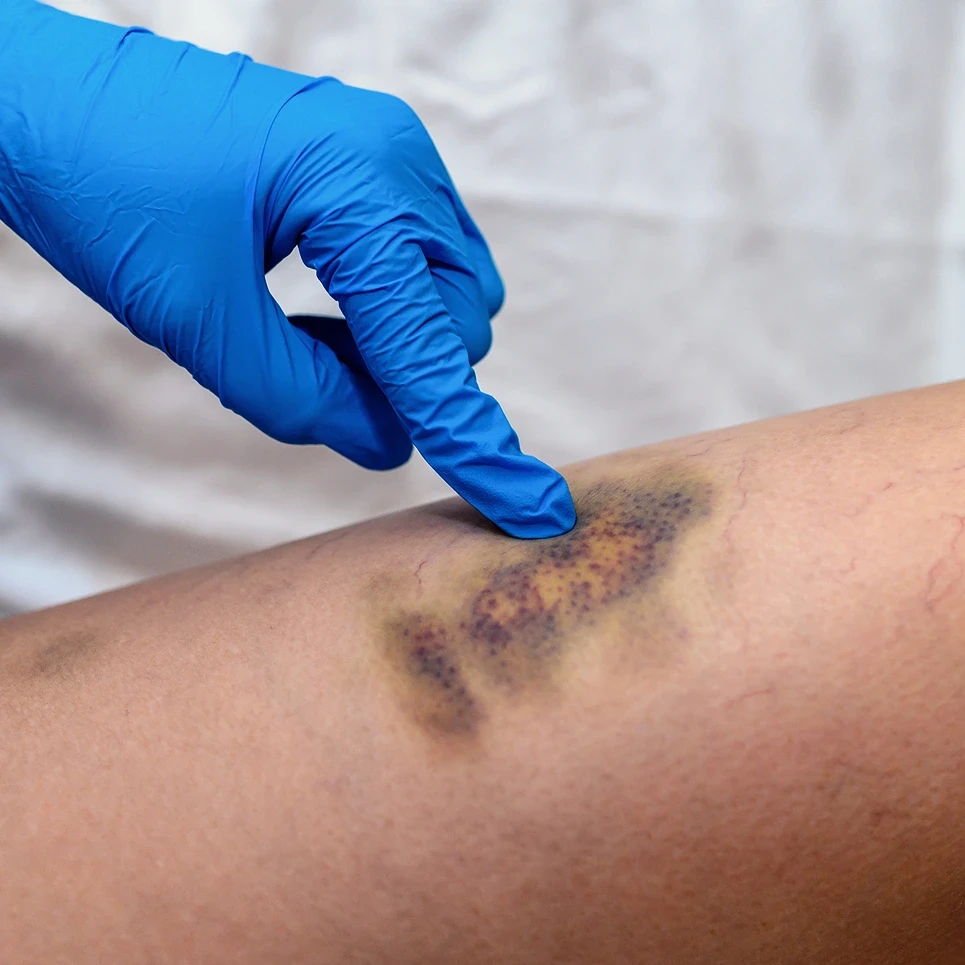
Allergic reactions to the sclerosing solution used in sclerotherapy, although rare, can occur and necessitate immediate attention. If you’re considering sclerotherapy for your spider veins, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential for an allergic response.
These reactions are generally mild and localized, similar to contact dermatitis, and often resolve on their own within a short period, typically 72 hours, as the sclerosing solution is quickly excreted from the body.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include itching, redness, and swelling at the injection site. In rare cases, more severe reactions can occur, such as anaphylaxis, which is a serious allergic reaction that can make it difficult to breathe.
This severe reaction is extremely rare but can be immediately treated by a well-trained doctor if it occurs during the procedure.
To minimize the risk of allergic reactions, your doctor may use advanced injection techniques and consider your patient sensitivities before administering the sclerosing solution.
If you have a history of allergies, it’s important to inform your doctor, as this can increase your likelihood of experiencing an allergic reaction to the agents used in sclerotherapy.
Your doctor may also perform a small patch test to check for any adverse reactions before proceeding with the full treatment.
Bruising and Swelling
Bruising and swelling are common side effects following sclerotherapy for spider veins. These reactions are typically temporary and manageable.
Bruising at the injection site is one of the most frequent side effects, and it usually resolves on its own within a few days. The bruising duration can vary, but it generally disappears within a couple of days to a week].
Swelling is another common side effect that can occur around the injection site. This swelling is often accompanied by redness and inflammation, which are natural responses to the sclerosing agent irritating the vein walls.
To manage swelling, wearing compression stockings immediately after the procedure can be highly effective. These stockings help reduce swelling by applying pressure that supports optimal blood circulation and prevents blood from accumulating in the leg veins.
In some cases, you might also experience tenderness and minor discomfort at the injection site, but these symptoms are usually mild and transient.
Following the recommended post-procedure instructions, such as avoiding certain medications and activities, can also help minimize the severity of bruising and swelling.
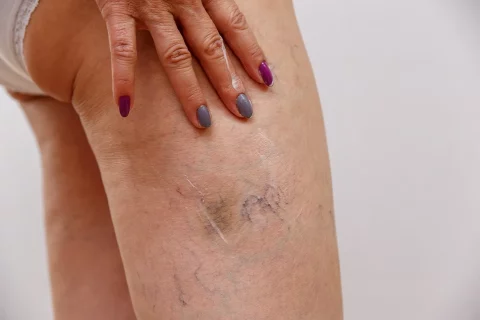
Skin Discoloration
Skin discoloration, or hyperpigmentation, is a common side effect of sclerotherapy, the procedure used to treat spider veins. This discoloration typically occurs because blood becomes trapped in the treated vein and is slowly reabsorbed by the body, leaving a brown or darkened area along the vein.
The duration of this discoloration can vary. Mild discoloration may resolve within 4 to 6 weeks, while more noticeable or extensive discoloration might take 3 to 6 months to fully disappear. In some cases, especially in patients with darker skin tones, the discoloration can last up to a year, although permanent hyperpigmentation is rare, affecting only about 1% of patients.
To manage and prevent skin discoloration, several strategies can be employed. Wearing compression stockings as directed can help improve circulation and reduce blood pooling in the treated veins.
Protecting the skin from sun exposure is crucial, as UV rays can exacerbate hyperpigmentation. Additionally, avoiding supplemental vitamins with iron and using topical treatments like vitamin C or hydroquinone can help minimize discoloration.
Following your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and maintaining patience as your body heals are also key to managing this side effect.
Serious Complications
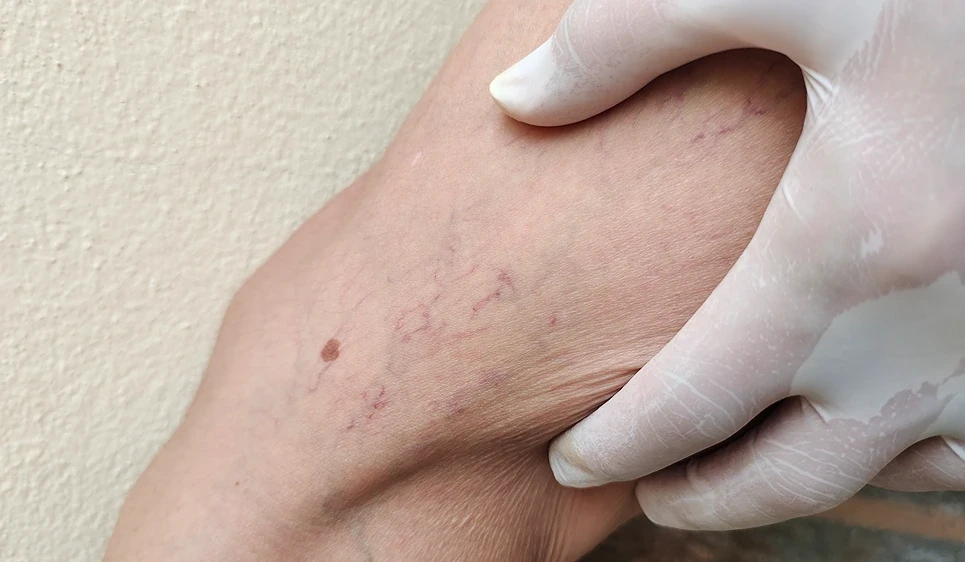
While skin discoloration is a common and generally manageable side effect of sclerotherapy, there are more serious complications that, although rare, can occur.
One of the most critical serious complications is an allergic reaction to the sclerosant used in the injections. This can range from mild symptoms like itching, redness, and swelling to severe reactions such as anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical attention. Anaphylaxis can cause difficulty breathing, and it’s crucial for the doctor to be prepared to administer emergency treatment promptly.
Another serious complication is the formation of blood clots, which can occur if the sclerosing solution is injected into a larger vein. These clots can be dangerous as they may travel through the bloodstream and cause a pulmonary embolism, leading to chest pain and breathlessness. It’s essential to monitor for these symptoms and seek emergency care if they arise.
Proper injection techniques and careful patient selection are key in minimizing these risks. Using ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy can help reduce the risk of intra-arterial injection, which can lead to severe complications like tissue necrosis.
Experienced practitioners are better equipped to handle these procedures safely and effectively.
Blood Clots and Phlebitis
When sclerotherapy goes awry, one of the potentially serious complications you might face is the formation of blood clots. This condition, known as phlebitis or superficial thrombophlebitis, involves inflammation of a vein near the surface of the skin due to a blood clot. The symptoms can include pain, tenderness, swelling, and warm, itchy skin over the affected area. The skin may also become red and hard, feeling like a cord-like structure.
Phlebitis can be a direct result of the sclerotherapy procedure, especially if the sclerosing solution is injected into a larger vein. This can cause the vein to become blocked, leading to blood clots.
Other risk factors that increase your chances of developing phlebitis include varicose veins, prolonged inactivity, obesity, smoking, and certain medical conditions like cancer or blood disorders.
To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to follow preventive measures. This includes adhering to your doctor’s pre- and post-operative advice, maintaining an active lifestyle to improve blood flow, and wearing compression stockings as recommended.
While the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT) from sclerotherapy is less than 1%, being vigilant for the warning signs of phlebitis and seeking medical help promptly can prevent more serious complications
Post-Treatment Care
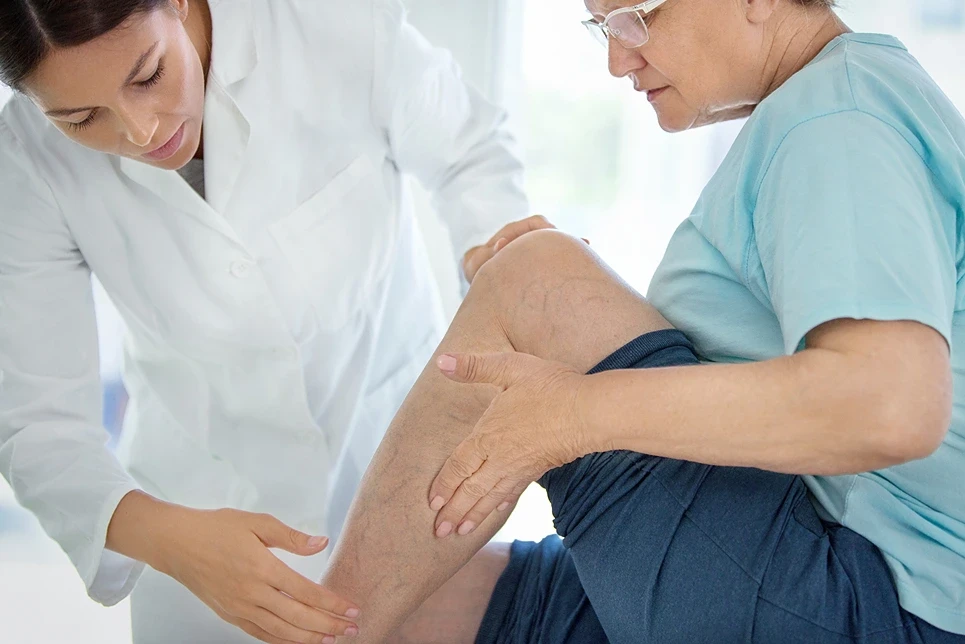
After addressing the potential risks of blood clots and phlebitis associated with sclerotherapy, it’s important to focus on the post-treatment care that can help minimize these and other complications.
Immediate Post-Treatment Care
Following sclerotherapy, you will need to adhere to several guidelines to ensure a smooth and effective recovery.
| Guideline | Details |
| Compression Garments | Wear medical-grade compression stockings for at least 3 days, and ideally up to 3 weeks, to keep constant light pressure on the treated area |
| Activity Restrictions | Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and prolonged sitting or standing for the first few days. Walking is highly recommended to improve blood circulation |
| Hygiene | Cleanse the treated area with soap and lukewarm water, but avoid hot baths, saunas, and steam rooms |
| Sun Exposure | Avoid direct sun exposure to the treated area until any bruising has resolved, and use sunscreen with at least 30 SPF when going outdoors |
| Follow-Up | Attend all follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and address any new spider veins |
Ongoing Care
In the weeks and months following the procedure, you may experience temporary side effects such as bruising, cramping, and dark lines or spots, which typically resolve within a few weeks. It’s crucial to elevate your legs above your heart for at least 30 minutes to reduce swelling and bruising.
Long-Term Outcomes
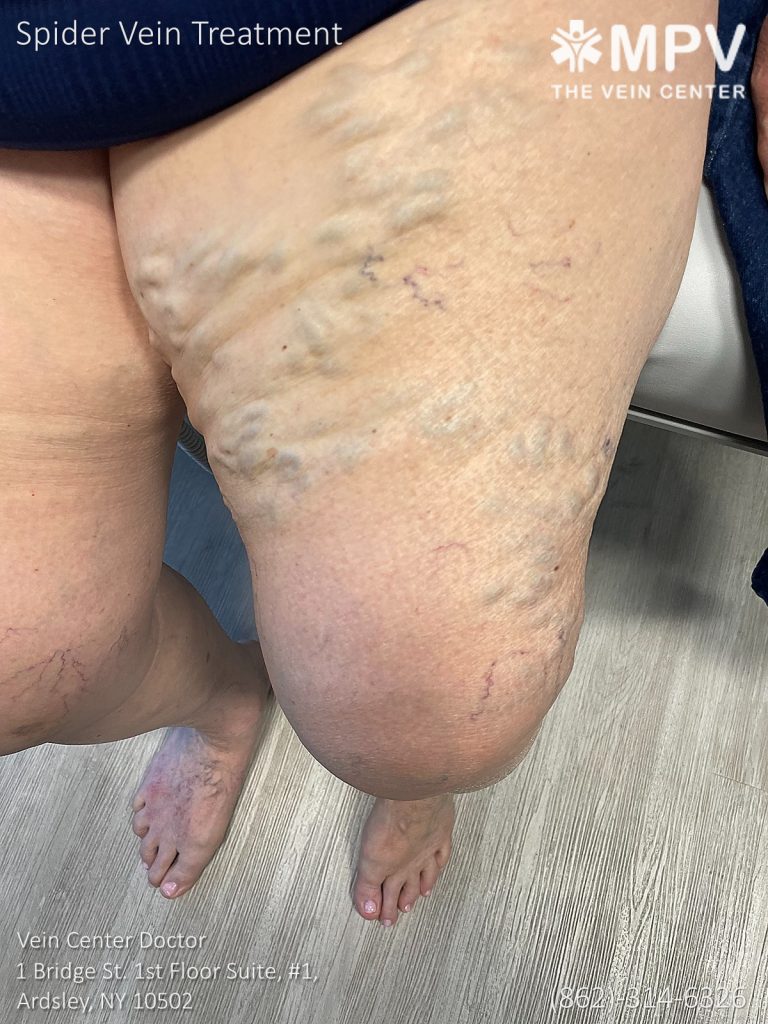
In the long term, sclerotherapy generally yields positive outcomes, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in the appearance and comfort of their treated areas. The long-term effectiveness of sclerotherapy is well-documented, with most veins either lightening or disappearing over time. You can expect a 70%-75% improvement in the appearance of your treated veins, which is a common reported satisfaction rate among patients.
The results of sclerotherapy are considered permanent for the treated veins, as these veins won’t return once they’ve been closed off by the sclerosant solution. However, it’s important to note that new varicose or spider veins can develop in other areas over time due to factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, and lifestyle choices.
Patient satisfaction with sclerotherapy is high, partly because the treatment is minimally invasive and allows for quick recovery. Most patients can resume their regular activities immediately after the procedure and experience full results within three to six months, depending on the size of the treated veins.
Dr. Sood at Vein Center Doctor is always happy to offer free consultations to anyone looking to understand their vein issues. Don’t spend another day wondering how to make those visible veins go away. Call us at 862-227-1143 today!