The varicose vein experience varies for each patient – some have mild discomfort, while others experience deep burning sensations. Nevertheless, it is essential to know what treatments can be done to help treat varicose vein pain. One of which is by taking an anti-inflammatory medication such as mefenamic acid.
So how does mefenamic acid help alleviate the pain associated with varicose veins? Mefenamic acid is a short-term treatment that can treat mild to moderate pain through its anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activities. Alternatives include medications from the same class of drugs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, among others.
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Mefenamic Acid
Mefenamic acid is prescribed for patients looking to relieve mild to moderate pain, including the discomfort associated with varicose veins, heavy menstrual bleeding, and arthritis.
It’s part of a class of medications called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) which halt the body’s production of cyclo-oxygenase enzymes, which produce prostaglandins, the substance that causes pain, fever, and inflammation.
Delving into the science behind varicose veins: veins are the highways of the body. They pump blood to various parts of the body, as well as back to the heart. The valves (or traffic signals) open and close to ensure that the blood flow is going in the right direction. Varicose veins refer to the condition of broken valves; blood flows backward causing it to pool. Taking NSAIDs helps reduce the swelling and pressure build-up caused by varicose veins.
How to Take Mefenamic Acid
Precautions
- Allergies: Mefenamic acid may put you at risk of anaphylaxis or severe allergic reaction. Call your doctor immediately if you experience itching, difficulty breathing, and swelling after medicine intake.
- Pediatric: Medical professionals don’t advise giving this medicine to children below 14 years old. This is due to the strength of mefenamic acid and the lack of research about possible side effects on children.
- Geriatric: Mefenamic acid and other NSAIDs increase the risk of heart attacks, stroke, and blood clotting, which may harm older patients. We advise you to inform your doctor beforehand of any known illness before receiving painkillers.
- Breastfeeding and pregnant women: Taking mefenamic acid while pregnant could harm the unborn baby through possible complications. For breastfeeding moms, it would be best to tell your doctor before intake.
- Ulcer and digestive illnesses: NSAIDs may cause stomach bleeding, anemia, and kidney and liver problems for patients with ulcers and other digestive illnesses.
Forms and Strengths
| Form | Strength |
| Oral capsules | 500 mg |
| 250 mg | |
| Suspension | 50mg/5 ml |
Special Dosing Considerations
Always follow your doctor’s recommended dosage of mefenamic acid. The standard dosage for acute pain (ages 14 and above) is 500 mg for the initial intake, then 250 mg every 6 hours after. Patients with heart disease and digestive conditions are given reduced dosage. Also, remember that mefenamic acid medication should not be used for more than 7 days.
How to Get the Most Out of Your Mefenamic Acid Treatment
Getting the most out of your mefenamic treatment will benefit you in more ways than one. Each type of medication – prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) – has advantages and disadvantages related to its use. You can boost possible benefits and lower potential hazards by taking the medication as prescribed.
1) Schedule Regular Appointments
Schedule and always show up to your follow-up appointments. This will help your doctor keep a close eye on your symptoms and see how your body is reacting to your varicose vein treatment. This is crucial, especially when you are using mefenamic acid, to make sure that the treatment’s healing potential is maximized.
2) Follow the Recommended Dosage
Always follow your doctor’s prescription. Never take your medication in excess of the recommended dosage, frequency, or duration so that you don’t experience an increased risk of stomach bleeding and other possible health conditions.
3) Drug Interaction
Carefully check the labels of the medicine before taking them. Many over-the-counter drugs contain painkillers (e.g., ibuprofen for venous conditions, tranexamic acid for dysmenorrhea) that could increase the risk of certain side effects. Ask the pharmacist whether the medications you are taking (or planning to buy) have interactions with mefenamic acid.
4) Storage of Mefenamic Acid
To get the most out of the medicine, store it in a dry place at room temperature, away from direct sunlight. Throw it away as soon as it expires. Never consume medicine at the risk to your health, especially when the medication is past its expiry date.
Possible Side Effects of Mefenamic Acid
All medications have side effects. NSAIDs, including mefenamic acid, are widely available and generally safe. While this class of drugs can interfere with blood clotting, their most serious side effects are bleeding and stomach pain. Some possible symptoms that can come with taking mefenamic acid include:
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- High blood pressure
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Swelling of feet
- Ringing in the ears
Important: Inform your doctor if you have consumed alcohol or any blood thinners before taking any type of NSAID. Let them know about any allergies, your medical history, and if you are pregnant. Some health-related factors may cause an increased risk of a serious blood clot and other fatal side effects.
Mefenamic Acid: Black Box Warning
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are one of the most prescribed medications in modern medicine. Given that mefenamic acid is part of this class of drugs, this means that it can potentially cause serious cardiovascular complications. This has led to a “black box” warning for NSAIDs.
1) Heart Risk Warning
NSAIDs are effective treatments for pain and inflammation. However, it can increase the risk of cardiovascular conditions. Patients who take NSAIDs (other than aspirin), especially those with a history of cardiovascular disease and heart attack, are more prone to experiencing complications as compared to people who do not take these medications. The risk is also higher for those who have been taking NSAIDs for a long period of time.
2) Stomach Problem Warning
Mefenamic acid, as well as other NSAIDs, increase the risk of adverse gastrointestinal events such as ulcers, bleeding, or holes in the stomach. The risk is higher for patients who are old, have poor health, and drink a lot of alcohol while taking mefenamic acid. It is crucial that you be transparent with your doctor about all the medications that you’re taking and if you’ve had any bleeding disorders.
Medication Treatments for Varicose Veins
Conservative treatments rely on medication – whether it’s over-the-counter or doctor-prescribed – to manage any pain, discomfort, or trauma caused by varicose veins. Just keep in mind that an overdose of these medications can take a toll on your stomach, livers, and kidneys. So always follow your doctor’s instructions. Keep in mind that this is not a complete list of possible medications for varicose veins.
| Drug Name | Description | Drug Class | Administration Routed | Standard Dosage |
| Aspirin | Aspirin is a preventative medication for those at risk of blood clots due to a faulty vein; however, the medication doesn’t treat the affected vein itself. It can also decrease fever, relieve pain, and reduce inflammation. | NSAID | Oral | Dosage varies depending on doctor’s prescription |
| Ibuprofen (Motrin) | Ibuprofen, similar to aspirin, is an oral medication prescribed for patients that want to deal with the discomfort of varicose veins. It can also be found in Advil and Nuprin. | NSAID | Oral | At least 200 mg every 4 to 6 hours |
| Naproxen (Aleve) | Naproxen is an over-the-counter medication that alleviates the pain and swelling brought about by varicose veins. It temporarily reverses the inflammation of vein valls (venous insufficiency). | NSAID | Oral | 500 to 750 mg once daily |
| Ketoprofen (Orudis KT) | Orudis KT thwarts your body’s production of certain substances that have inflammatory effects. Consequently, it can treat pain, swelling, and joint pain. | NSAID | Oral | 75 mg 3 times a day or 50 mg 4 times a day |
| Meloxicam (Mobic) | Meloxicam belongs to a newer classification of anti-inflammatory drugs called Cox-2 inhibitors. While it may not be as strong as other prescription-only NSAIDs, it can provide pain relief for a longer period of time. | NSAID | Oral | 7.5 mg once daily |
| Acetaminophen (Tylenol | This is a pain relief medication for varicose veins, menstrual bleeding pain, colds, sore throats, and fever. It does not, however, reduce inflammation. | Analgesic | Oral | 650 mg every 4 to 6 hours |
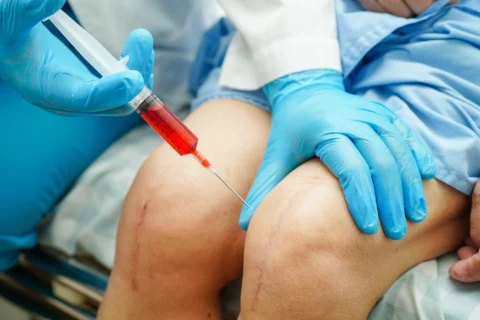
| Polidocanol (Asclera) | Polidocanol foam sclerotherapy is an effective method for treating small varicose veins. You can return to your normal activities right after your treatment. | Sclerosing agent | Intravenous injection | Dosage varies depending on size and extent of varicose vein |
| Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate (Sotradecol) | This sclerosing agent is injected into a damaged vein in the lower extremities. | Sclerosing agent | Intravenous injection | Dosage varies depending on size and extent of varicose vein |
Lifestyle Changes for Varicose Veins

1) Leg Elevation
Sitting or standing for long periods of time in the same position can cause varicose veins. If your job requires you to sit or stand all day long, try to change position multiple times a day. When sitting down, elevate your legs with a footstool or flex and bend them to increase blood flow.
2) Exercise
Exercising not only gives you a healthy body but also healthy veins. As simple as taking the stairs instead of an elevator or allotting 20 to 30 minutes of your time walking can increase circulation in your legs. Remember to avoid certain types of exercises that place excess pressure on your veins such as lifting weights and high intensity running.
3) Healthy Diet
Avoid consuming foods that are high in sodium as this mineral increases fluid retention, which then puts pressure on your veins and leads to swelling. Instead, you can make dietary substitutions. Switch out white flour for whole wheat. Replace white rice with brown rice. Avoid processed and refined sugar. Rutin-rich foods (e.g., blackberries, apples, apricots, grapes) can also alleviate varicose vein pain.
4) Proper Clothing
We highly recommend that you wear loose-fitting, comfortable clothing if you have a venous condition. Restrictive and tight clothing, such as girdles and body shapers, can restrict blood flow and exacerbate varicose veins.
High heels can also aggravate varicose veins, especially when you wear them for long periods of time. Opt for shoes with good arch support to relieve any pain or discomfort. A stylish flat could also be an option to keep your legs healthy.
5) Moisturize the Skin
Applying moisturizer twice a day to your legs can heal dry or cracked skin. This can also maintain the elasticity of your skin and support cell walls. This way, you can decrease the visibility of your varicose veins and enhance vein health.
Reliable Medical Procedures from Vein Center Doctor
1) Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is often considered the medical treatment of choice for small varicose veins. The doctor will slowly inject a sclerosing agent, usually in liquid form, directly into the appropriate vein, causing it to collapse and block blood flow. The treated vein eventually fades within a few weeks.
2) VenaSeal
This is one of the best varicose vein treatments available at Vein Center Doctor. During a VenaSeal procedure, the doctor makes a map of the damaged veins then administers a medical adhesive to close them. Blood flow is then redirected to the healthy veins. You can resume regular activities the day after your treatment.
3) Venous Compression Therapy
Compression therapy involves wearing compression stockings on the legs to enhance blood flow in your lower extremities. It can help alleviate symptoms of varicose veins, spider veins, and deep vein thrombosis, among other venous conditions. It can also complement other vein treatments.
4) Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Varicose Veins
RFA is a minimally invasive treatment for varicose veins. Its technique involves radiofrequency energy – instead of laser energy – to close off blood flow in the main problem vein. Your doctor will then use duplex ultrasound during your follow-up session to ensure that the vein was closed.
Get a Personalized Varicose Vein Treatment at Vein Center Doctor

Varicose veins cause all kinds of discomfort: itching, inflammation, and tired legs, among others. A combination of anti-inflammatory medication and medical procedures can eliminate the pain. Consider getting evaluated by a qualified vein specialist at the Vein Center Doctor and learn more about the best treatment options for your vein condition. Schedule a consultation today.